Bit Manipulation & Bitwise Operators
Bit manipulation
Bit manipulation is the act of algorithmically manipulating bits or other pieces of data shorter than a word. In computers every information is stored in the form of bits. A bit (Binary digit) stores either the value 0 or 1. Computer is an electrical device and all electrical devices understand signals, which are represented using two states.
To understand the bit system, consider an example of an electric bulb. An electric bulb has two states: either the bulb is on or off. If electric signals passed then bulb is on and if no signals passed then bulb is off which is represented as 1 (for on) and 0 (for off) in binary digit system.
In Simple words Binary Numbers are the flow of information in the form of zeros and ones used by digital computers and systems.
Bit Manipulation Operators
| Operator | Name | Usage | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| & | Bitwise AND | num1 & num2 | 7 & 10 | 2 |
| | | Bitwise OR | num1 | num2 | 7 | 10 | 15 |
| ^ | Bitwise XOR | num1 ^ num2 | 7 ^ 10 | 13 |
| ~ | One's Compliment (or) Unary Operator | ~ num1 | ~ 7 | -8 |
| << | Left Shift | num1 << 2 | 7 << 2 | 28 |
| >> | Right Shift | num1 >> 2 | 7 >> 2 | 1 |
Bitwise AND
The bitwise AND operator takes two operands as input. If both operands are 1 then the output of AND operator is 1 and if any one operand is 0, then the output of bitwise AND is 0.
| X | Y | X & Y |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
1Eg : num1 = 7 and num2 = 102Binary representation of 7 is 0 0 1 1 13Binary representation of 10 is 1 0 0 1 045Bitwise AND operation of 7 and 10 is as follows :677 = 0 0 1 1 1810 = 1 0 0 1 097 & 10 = 0 0 0 1 01011Decimal representation of binary number 0 0 0 1 0 is 2.12So 7 & 10 = 2
Bitwise OR
The bitwise OR operator takes two operands as input. If any one operand is 1 then the output of the bitwise OR operator is 1 and if both operands are 0, then the output of bitwise OR is 0.
| X | Y | X | Y |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
1Eg : num1 = 7 and num2 = 102Binary representation of 7 is 0 0 1 1 13Binary representation of 10 is 1 0 0 1 045Bitwise OR operation of 7 and 10 is as follows :67 = 0 0 1 1 1710 = 1 0 0 1 087 | 10 = 1 0 1 1 1910Decimal representation of binary number 1 0 1 1 1 is 15.11So 7 | 10 = 15
Bitwise XOR
The bitwise XOR operator takes two operands as input. If one of the operands is 1 then the output of the bitwise XOR operator is 1 and if both operands have the same bit(either 0 or 1), then the output of bitwise XOR is 0.
| X | Y | X ^ Y |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
1Eg : num1 = 7 and num2 = 102Binary representation of 7 is 0 0 1 1 13Binary representation of 10 is 1 0 0 1 045Bitwise XOR operation of 7 and 10 is as follows :67 = 0 0 1 1 1710 = 1 0 0 1 087 ^ 10 = 1 0 1 0 1910Decimal representation of binary number 1 0 1 0 1 is 13.11So 7 ^ 10 = 13
Bitwise 1’s Complement
Bitwise Complement operator is an unary operator which works on only one operand. This operator inverts the binary bits. It means if the operand is 0 then the bitwise complement operator changes the value of operand to 1, and if the operand is 1 then the bitwise complement operator changes value of operand to 0.
| X | ~X |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
Left Shift Operator
Left shift operator is a binary operator which also needs two operands. Left shift operator shifts all bits of the first operand towards the left by the number of positions specified by the second operand. Left shift operator is denoted using symbol << and the usage of left shift operator is variable << number_of_positions where variable is the first operand and the number_of_positions is the second operand.
Eg: 36 >> 1 = 18
136 << 1 = 72 = 36 * 2 = 36 * 2^1236 << 2 = 144 = 36 * 4 = 36 * 2^234.5.6.7836 << n = 36 * 2^n
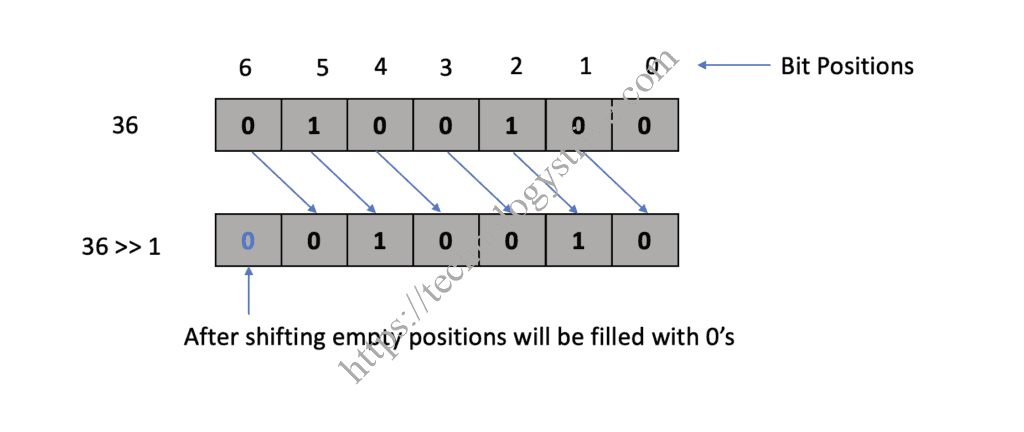
Right Shift Operator
Right shift operator is a binary operator which also needs two operands. Right shift operator shifts all bits of the first operand towards the right by the number of positions specified by the second operand. Right shift operator is denoted using symbol >> and the usage of Right shift operator is variable >> number_of_positions where variable is the first operand and the number_of_positions is the second operand.
Eg: 36 >> 1 = 18
136 >> 1 = 18 = 36 / 2 = 36 / 2^1236 >> 2 = 9 = 36 / 4 = 36 / 2^234.5.6.78 36 >> n = 36 / 2^n
Code Implementation
- Java
- C
- Python
1public class BitWiseOperators {23 public static void main(String[] args) {4 int num1 = 7 ;5 int num2 = 10;67 System.out.println(num1+" & "+num2 +" = "+(num1 & num2));8 System.out.println(num1+" | "+num2 +" = "+(num1 | num2));9 System.out.println(num1+" ^ "+num2 +" = "+(num1 ^ num2));10 System.out.println("~"+num1 +" = "+(~num1));1112 int num = 36;13 System.out.println("36 << 1 = "+ (num << 1));14 System.out.println("36 << 2 = "+ (num << 2));1516 System.out.println("36 >> 1 = "+ (num >> 1));17 System.out.println("36 >> 2 = "+ (num >> 2));18 }19}